The pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by the true pathogen acute coronavirus respiratory syndrome 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has had a profound impact on the lives of people all over the world for nearly year. Since this disease was diagnosed in December 2019, it has taken over 2.2 million lives. At the same time, great economic pressures have come from the severe restrictions placed on human movement and physical interactions outside one’s own family or family to keep the spread of the virus at bay.
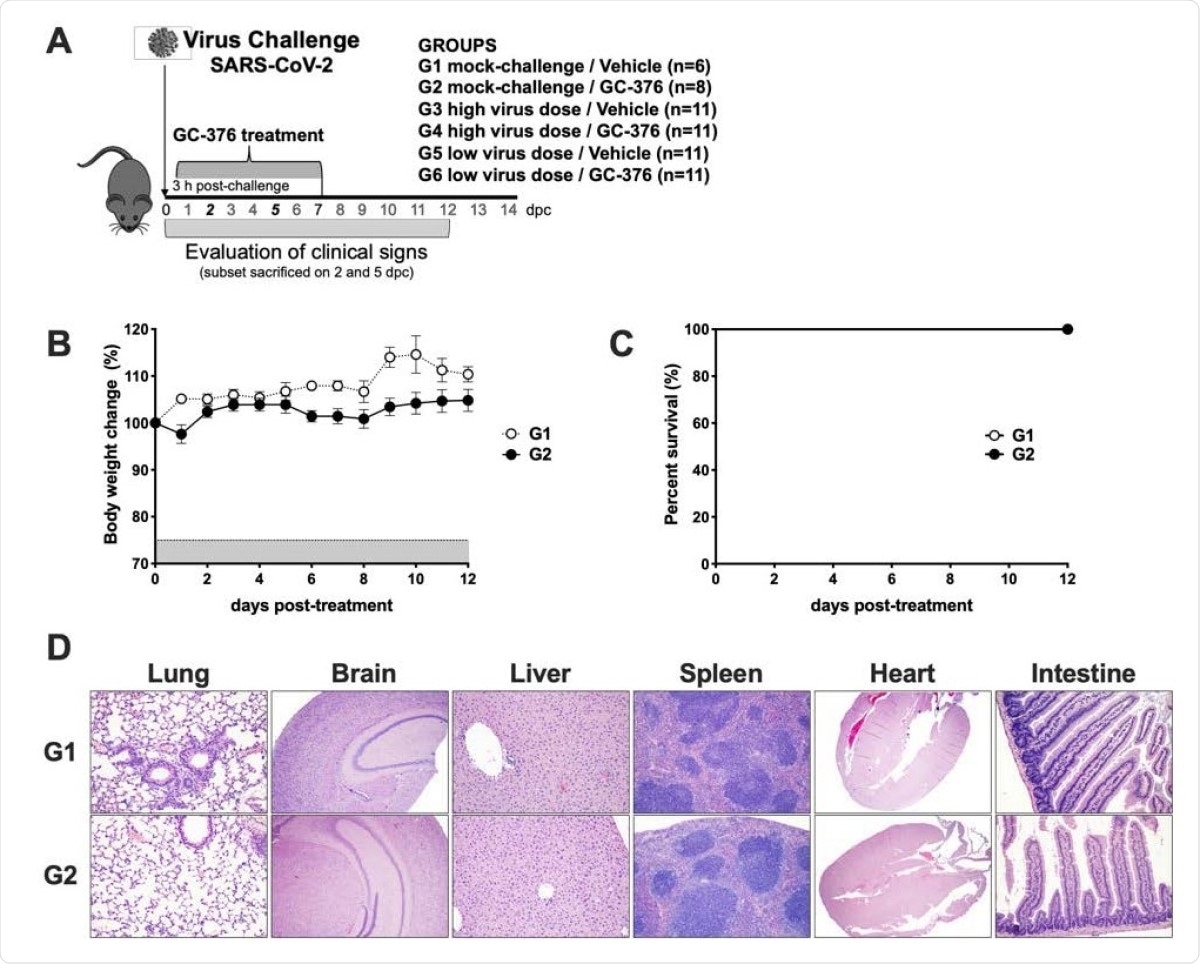
Decorative representation of experimental design and evaluation of GC-376 safety in K18-hACE2 mice. (A) K18-hACE2 was either challenged (G1 and G2) or challenged with SARS-CoV-2 at high dose virus (1×10ˆ5 TCID50 / mouse; G3 and G4) or low virus dose (1×10ˆ3 TCID50 / mouse; G5 and G6). IP handling with vehicle (G1, G3, and G5) or GC-376 (G2, G4, and G6, 40mg / kg day). Subsets of mice were humanized at 2 and 5 dpc and different tissues were collected. Mice (n = 8) received 40mg / kg of GC-376 dose in two daily doses for 7 days and (B) weight changes and (C) were monitored for 12 days. (D) Mice were excreted humanly at 14 dpc and lungs, brain, liver, spleen, heart and SI were collected. HE slides were generated and analyzed compared to the negative control group. Representative images were taken at 20X size for all materials except brain samples taken at 4X.
Evaluating GC-376 in vivo
The most feasible way to contain this virus is to vaccinate the global population, which has led to accelerated development and release of several COVID-19 vaccines. Over the past few months, many antivirals have been identified that deserve further development to target several viral proteins. A recent introduction to the bioRxiv * server reacts with one such molecule, the major viral protease inhibitor (Mpro) GC-376.
While in vitro studies have confirmed that inhibition of SARS-CoV Mpro in the presence of GC376, and its potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity, has not been proven, like other Mpro protectors, in vivo. The current paper aims to outline the in vivo GC-376 antiviral activity.
Study details
The researchers used the K18-hACE2 transgenic mouse model, which involves mice modified by the induction of the type 2 angiotensin-converting enzyme receptor (hACE2) under the control of the keratin promoter 18 .This animal model develops the clinical and fatal disease after challenge with the SARS-CoV-2.
The researchers challenged the mice with two different viral doses of SARS-CoV-2. Challenges were controlled. Three hours after the viral challenge, the mice were treated with GC-376 or vehicle for seven days.
The defiant mice showed no adverse effects whether treated with the vehicle or GC-376. The mice treated with GC-376-exposed virus developed dose-dependent effects of clinical disease.
Mice in the high-dose, untreated challenge group either died or became so severe that they were introduced. In the high-dose challenge group with GC-376 treatment, results were similar, but one in five mice survived. Although this difference was unsuccessful, body weight loss between the two groups was quite different.
In the untreated low-challenge group, disease progression occurred although at a slower rate, reflecting a dose-dependent effect on viral challenge. Eventually, 60% of mice survived defecation. However, there was no clear improvement in clinical outcome of mice in the treated and untreated low-challenge GC-376 groups, indicating that the drug has only a small benefit in terms of clinical signs and outcome.
Lower viral load in mice treated with GC-376
The researchers found that mice treated with GC-376 showed high levels of replication in several organs. The viral titers in many substances increased over time, indicating systemic transmission.
However, the brain samples in GC-376-treated groups showed lower virus loads, although the difference between individuals in the treatment groups showed low GC-376 virus challenge. In this group, the viral load in the brain was often indeterminate, but this was not associated with higher survival compared with controls.
Toxic deficiency
A close examination of various tissues in infected mice shows that GC-376 does not emit major poisoning, but on the other hand, the drug may reduce the degree of inflammation and tension damage caused by GC-376. caused by a virus after infection.
What is the impact?
The researchers note that high virus resistance caused severe disease and similar lethal outcome, delayed infection and 60% survival in the low virus challenge group. This study confirms the suitability of this transgenic mouse model as a platform to evaluate disease outcomes and host responses, even though the lethal methods may not correspond to those operating in humans.
The study also demonstrates the safety of GC-376. The low-drug-treated virus challenge groups showed only small differences in clinical signs, weight loss, and survival from open controls. However, other findings include the presence of lower viral loads, milder thin lesions and less swelling compared to open controls.
The lowest viral loads in the brain after GC-376 treatment are important because neurological involvement has been observed in many COVID-19 patients, and are associated with severe acute exacerbation in two-thirds of cases. .
The milder lesions and the seemingly favorable effect of GC-376 on virus-induced inflammation may also be important, as the immune response is thought to be irregular with multiple inflammation. -systematic is a major and often fatal complication of COVID-19.
The researchers suggest that this indicates that GC-376 may be an SARS-CoV-2 antiviral in vivo. His mediocre activity was expected from his mediocre activity in vitro. The effectiveness had to be improved ten to one hundred times to demonstrate useful therapeutic activity.
This may be possible by making good use of the structure of the cement, using higher doses or by combining it with other antivirals or anti-inflammatory drugs such as dexamethasone. Future studies would be helpful.
* Important message
bioRxiv publish preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be seen as final, guiding health-related clinical practice / behavior, or be treated as information established.