Many vaccines have been developed to promote immunity against severe respiratory syndrome (SARS-CoV-2). However, storage is a major concern during vaccine distribution, especially in countries where specific freezers are scarce.
A new study reports positive results from two new vaccine candidates. The study, led by Axel T. Lehrer of the University of Hawaii at Manoa, examined the immune response of mice when administering the adjuvant CoVaccine HT with SARS-CoV-2-induced spike protein ectodomines.
“The immunosuppressive candidates test both antibody and cellular immunity with T helper (Th) type 1 and 2 helper in an outdoor mouse model…”
Future studies in humans may help develop a stable coronavirus vaccine that does not require cooling. This could lead to significant immunization efforts and increased immunity to viruses that have spread in several countries around the world.
The study “SARS-CoV-2 regenerative protein vaccine induced by CoVaccine HT adjuvant stimulates broad-spectrum, Th1-mediated, and cellular immune responses in mice” is available as a preview of the bioRxiv* server, while the article is under peer review.
Optimizing vaccine dosages
Researchers tested vaccine immunity in Swiss male and female mice Swiss 7- to 10-week-old. They were administered intramuscularly, SARS-CoV-2 ectodomain SdTM or SdTM2P spike proteins alone or in combination with 1 mg of CoVaccine HT diagnostic treatment starting on day 0 and day 21. No the control but the confessional treatment.
To determine which dose provided the most significant immune boost, they administered 5, 2.5, or 1.5 micrograms of the ectodomine spike protein and 1 milligram of the adjuvant treatment. One group received 5 micrograms of SdTM2P with 0.3 milligrams of the adjuvant treatment.
The researchers examined antibody levels in serum samples on the 7thth, 14th, 28th, and 35th days after vaccination.
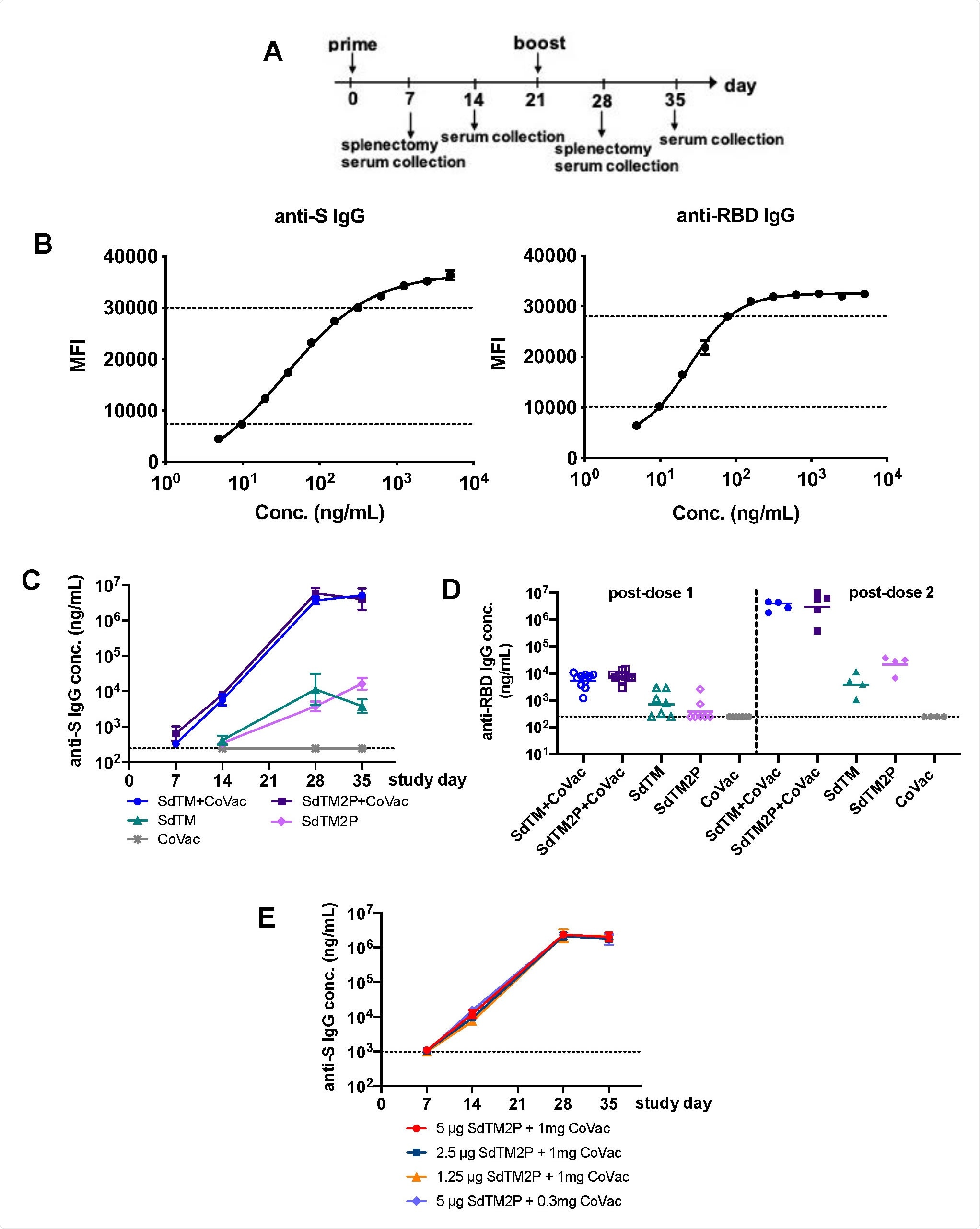
IgG antibody responses to reconstituted proteins SARS-CoV-2 S. (A) Groups of Swiss Webster mice (n = 7 or 15) were vaccinated with one or two doses of recombinant proteins with or without CoVaccine HT ™ (CoVac) at 3-week intervals. Sera was collected 1 and 2 weeks after each vaccination (days 7, 14, 28, and 35), and spleens were harvested 1 week (days 7 and 28) after each vaccination. SARS-CoV-2 S-specific IgG titers were measured by microsphere complex immunoassay (MIA) using SdTM2P and RBD-F linked beads. (B) The pur-anti-S antibody was attenuated to concentrations in the range of 4.8 to 5000 ng / mL and examined by MIA as standard (as described in the Materials and Methods). Sera mice were evaluated along with the antibody level and the IgG concentrations were placed between the normal loops using a computer model of sigmoidal dose response (GraphPad Prism). The dotted lines indicate the top and bottom of a serial field used to separate antibody concentrations (C) The anti-S and (D) anti-RBD antibody titers in sera from mice vaccinated with SdTM or SdTM2P ( purified with hACE2 AC) with or without adjuvant or (E) anti-S antibody in serum of mice administered various dosages (5, 2.5, or 1.25 μg) of SdTM2P (purified with mAb IAC) with adjuvant (1 or 0.3 mg) expressed as IgG (ng / mL) concentrations. The dotted lines in panels C to E mark the base of the linear field of the normal curve.
Immunity seen in all mice provided the combination treatment
Spike protein-specific immunoglobulin antibodies were observed in the serum of mice after vaccination with the CoVaccine HT adjuvant and the spike protein ectoderm. Antibody levels were higher with the ectoderm / adjuvant protein spike treatment compared to the ectoderm spike protein alone.
The administration of two doses of the immunoglobulin-enhanced antibody mixture treatment was also specific to spike protein binding domain, which is a target for neutralization of antibodies.
Vaccine-induced antibody levels were not altered by lower doses of either the spike protein ectoderm (2.5 or 1.25 micrograms) and the adjuvant CoVaccine HT (0.3 milligrams).
Neutral antibody titers were also measured and were higher in mice that received the combined vaccine.
Antibody titers were dose dependent. There was a marked shift of neutral titers when mice received lower dosages of SdTM2P proteins.
However, overall efficacy does not appear to be altered by a lower dose.
The researchers write:
“Note that the serum PRNT50 titers of mice receiving a lower (0.3 mg) amount of CoVaccine HT were comparable or even higher than those in mice given 1 mg of confection, which ‘shows that the optimal vaccine formulation can be achieved by using lower dosages of confession. The results show that as little as 2.5 mg of protein S antigen with 0.3 mg of adjuvant may be sufficient to induce strong neutralizing antibody responses. “
Vaccines stimulate different immune responses
The researchers assessed the balance of Th1 and Th2 immune responses because an imbalance of Th2 has been linked to vaccine-associated advanced respiratory disease. They compared S-specific IgG2a / b levels and IgG1 to assess the ratio between Th1 and Th2.
Results showed higher ratios of IgG2a / IgG2b in mice with the combination vaccine, suggesting th1 immune responses.
They also evaluated the number of IFN-g-secreting cells to assess T cell responses. One and one dose of the combination vaccine produces IFN-g-secreting cells.
Although, by reducing the amount of enhanced SdTM2P proteins or a lower dose of 0.3 milligrams of CoVaccine HT, it appeared to reduce the number of IFN-g secretory cells. However, the researchers say this finding was not statistically significant.
* Important message
bioRxiv publish preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be seen as final, guiding health-related clinical practice / behavior, or be treated as information established.