
A team of international scientists has recently studied the effectiveness of PVP-1, a complex of polyvinylpyrrolidone and iodine, in preventing severe coronavirus syndrome 2 (SARS-CoV-2) disease. Using in vitro cell culture conditions, the scientists maintain that PVP-1 formulation used in commercially available nasal spray (Nasodine) readily exerts SARS-CoV-2 side effect. short-term interior. The study is currently available on the bioRxiv* preprint server.
Background
Coronavirus 2 of severe respiratory syndrome (SARS-CoV-2), the causative pathogen of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), is spread mainly from person to person through large respiratory droplets. However, there is evidence to suggest that it is possible to transmit the virus in the air. The virus is known to reproduce more efficiently in the upper respiratory tract than in the lower respiratory tract. Two host cell proteins, namely angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2) and transmembrane serine protease 2 (TMPRSS2), which are essential for the viral envelope – host cell membrane fusion and viral entry, are expressed to large in the nasal and alveolar epithelial cells. , supporting the fact that viral reproduction is selective in the upper respiratory tract.
Since viral excretion from the nasal passages and upper respiratory tract are the main means of spreading disease, early elimination of SARS-CoV-2 in the nasal cavity can significantly reduce the risk of human transmission to person as well as multiplication of the infection to the lower respiratory tract and other organs.
In the present study, the scientists have investigated the efficacy of PVP-1 in the eradication of SARS-CoV-2 infection by making a series of in vitro tests. PVP-1 is known to have a wide range of non-chemical effects and is routinely used as a skin and mucous membrane protector. In this study, the scientists have specifically evaluated the efficacy of the nasal spray nasodine antiseptic Nasodine, which contains a clinically agreed formulation of 0.5% PVP-1.
Study design
Out of two SARS-CoV-2 isolates used in the study, one was ingested with Nasodine for 1 min. The other was stimulated with Nasodine or 0.5% PVP-1 in saline for 15 seconds, 5 minutes, or 15 minutes. Both PCR and cell culture-based methods were used to quantify the residual viral titers and to test the efficacy of PVP-1 composition.
Important comments
By making the assay based on cell culture, the scientists noted that Nasodine can completely inhibit the reproduction of SARS-CoV-2. In contrast, strong reproducibility was observed for SARS-CoV-2 treated with control media (without Nasodine).
For further testing, the scientists used a cytopathic-based assay (CEP) assay to test the effects of Nasodine on different SARS-CoV-2 strains. Two time points (15 seconds and 5 minutes) were considered clinically relevant for nasal use, since PVP-1-based nasal formation activity gradually declines with time due to iodine inactivation by nasal proteins.
The assay results showed that Nasodine significantly reduces SARS-CoV-2 reproduction within 15 seconds of exposure. In addition, no susceptible virus was detected after 15 minutes of treatment. Importantly, Nasodine formulation showed comparatively better efficacy than PVP-1 preparation in saline in reducing viral titers. The efficacy of Nasodine formation was higher at all clinically relevant time points (15 seconds and 5 minutes).
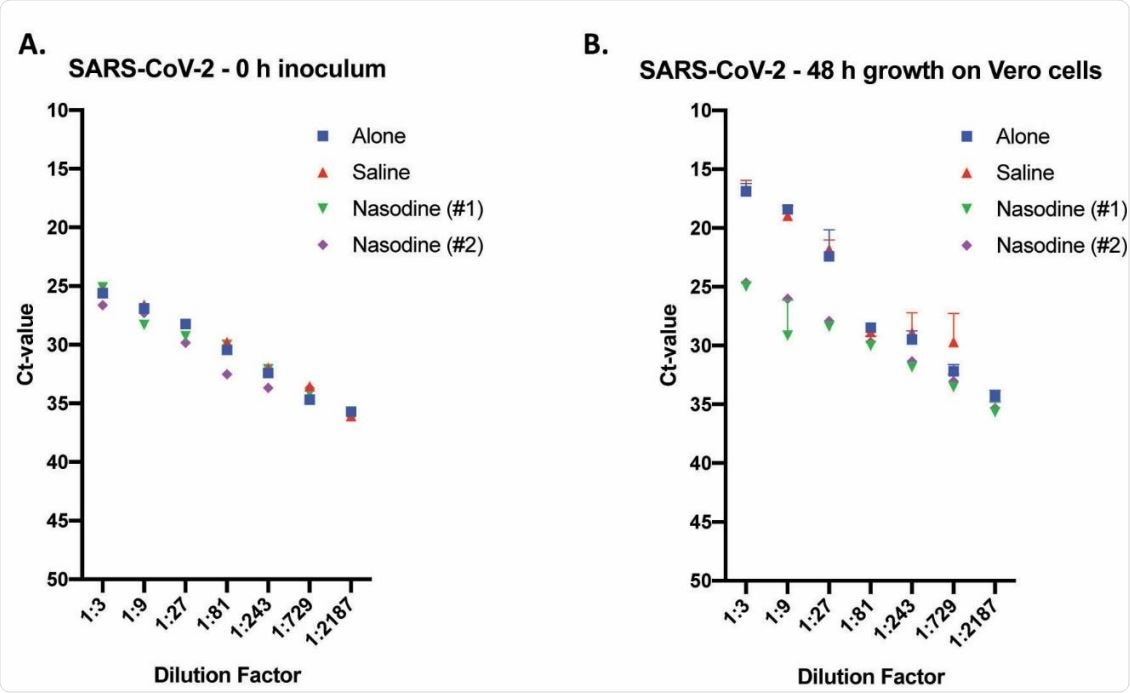
Titre de Nasodine and SARS-CoV-2 were treated with control via TCID50 assay and RNA detection via real-time TaqMan RT-PCR. SARS-CoV-2 was exposed to the designated test solution (s) for 1 min before serial attenuation (1: 3) and incubation of Vero cells for either 0 (zero) or 96 h. Values expressed as average cycle threshold (Ct) value + SEM (n = 3) against reduction factor. (A) Time level of zero (0 h) inoculum titration was used to determine baseline Ct values of manipulative samples before reproduction in Vero cells. (B) Cultivated titers would harvest 96 h after inoculation of Vero cells.
Investigate meaning
The study reveals that Nasodine, a clinically approved nasal spray formulation with 0.5% PVP-1, has significant antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2, and can be used for early elimination of SARS -CoV-2 in the nasal cavity. To better control COVID-19 pandemic, Nasodine can be used in combination with other control measures to prevent viral transmission.
The scientists are currently conducting a clinical trial to determine if these are the case in vitro effects are equally relevant for COVID-19 patients. They believe that Nasodine may be an effective supportive intervention for newly diagnosed COVID-19 patients in terms of reducing disease progression and viral peeling.
* Important message
bioRxiv publish preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be seen as final, guiding health-related clinical practice / behavior, or be treated as information established.