.jpg)
A new preclinical study led by Wensheng Wei of Peking University in China has developed a circular RNA vaccine recommendation. Their findings showed that the cyclic RNA vaccine produces neutral antibodies and strong T-cell responses against receptor binding domain of true spike coronavirus syndrome 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
The cyclic RNA vaccine also effectively neutralized the mutated receptor binding domain found in version B.1.351. The B.1.351 variant was first detected in South Africa and may bypass the immune system.
The currently approved messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines from Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech were developed before the variables appeared, so information is limited. The Johnson & Johnson vaccine was one-shot effective against the initial snoring in Wuhan, China, and the B.1.1.7 variant was first reported in South London last fall.
The results may help address the B.1351 variant and other anxiety changes.
The authors write:
“Because S48-CoV-2 mutations encoding E484K or N501Y or the K417N-E484K-N501Y escape neutral antibodies induced by mRNA vaccines, we hypothesized that virus effect on decoy HACE2 encoded circRNA. “
The study “Cyclic RNA Vaccines Against SARS-CoV-2 and Emerging Variants” is available as a preview of the bioRxiv* server, while the article is under peer review.
Development of the cyclic RNA vaccine
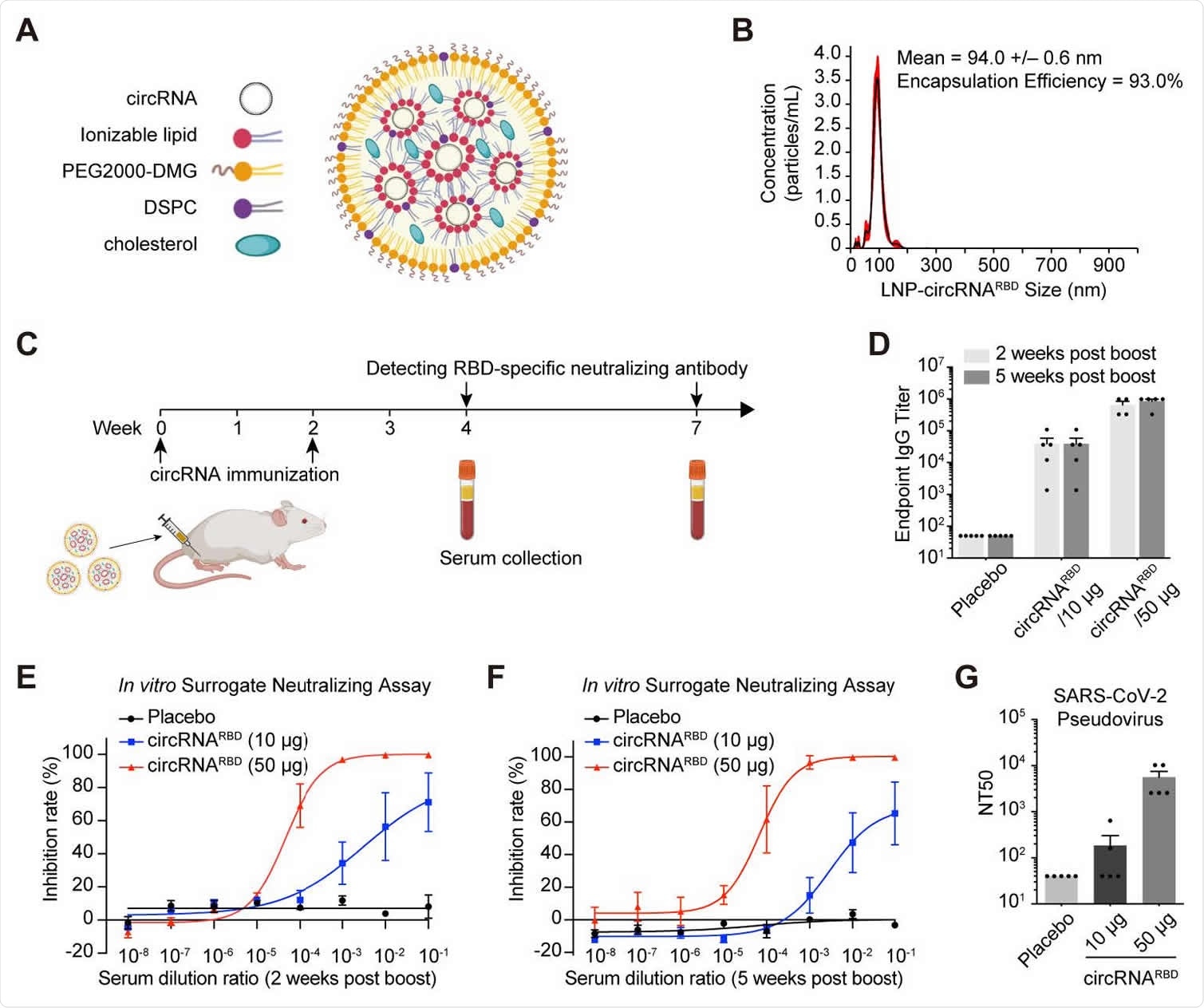
The team used a Group I ribozyme autocatalysis strategy to extract round RNA-coding antigens specific to the receptor binding domain at SARS-CoV-2 (circRNA).RBD). A series of peptide markers have been added to the N-terminus of the binding domain due to its secretory mechanism against antigens.
The IRES element was set prior to the receptor binding domain coding sequence to initiate translation. IRES-SP-RBD-T4 sequence was added to the circular vector to produce circRNARBD.
A circular RNA model shows high protein sensitivity and thermal stability
Their cyclic RNA model was more stable against RNAase R than serial RNA. When the circRNA is purgedRBD placed in HEK293T cells, they found many antigens – 50-fold larger than serial RNARBD groups specific to the receptor binding domain of SARS-CoV-2. These antigens prevented SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus infection.
They also showed high thermal stability. When stored at room temperature before being transferred into HEK293T cells, circRNARBD continues to show sensation two weeks after storage.
Strong immune response in mice
Mice were ingested intramuscularly with 10 μg or 50 μg of experimental circRNARBD vaccination at two-week intervals. Immunity was measured two to five weeks after their increased burn.
The titers of immunoglobulin G (IgG) and antibodies were expressed in a dose-dependent manner and continued for two to five weeks after their elevated burn. It also effectively neutralized the pseudovirus SARS-CoV-2. The researchers recommend the circRNARBD vaccine creates a persistent immune response against SARS-CoV-2.
When evaluating CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell immune responses after vaccination, the researchers found responses with Th1-induced interferon-γ (IFN-γ), tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α), and interleukin-2 (IL-2). ). However, no changes in interleukin-4 (IL-4) were observed. The results of the cyclic RNA vaccines stimulated the Th1 immune response but not Th2.
There were also several cytokine-producing CD8s+ found in circRNARBD vaccine mice. Interestingly, the team also found stronger immune responses in CD4 + and CD8 + memory T cells at 10 μg than 50 μg. Although, 50 μg induced a higher potency of neutralizing antibodies in B cell responses.
Cyclic RNA vaccine is effective in neutralizing the B.1.351 variant
The team collected the serum of vaccinated mice 1 and 2 weeks after their booster dose. They found specific IgG titers for spike protein receptor binding domain with the 501.YV2 trend.
The researchers then evaluated the neural activity of mice with the circRNARBD no circRNARBD-501Y.V2 vaccines against alterations D614G, B.1.1.7 / 501Y.V1, or B.1.351 / 501Y.V2. The circRNARBD Vaccine antibodies effectively neutralized all three viral strains with the highest activity against the D614G strain.
On the other hand, the circRNARBD-501Y.V2 also neutralizes all species, with the highest neutralization activity against the corresponding variable, 501Y.V2.
“It is worth noting that both vaccines could neutralize all three rays even though they had variable efficacy. However, the multiple vaccines should give both SARS-CoV better protection -2 indigenous and their circulation variables, “the research team wrote.
* Important message
bioRxiv publish preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be seen as final, guiding health-related clinical practice / behavior, or be treated as information established.