
The rapid spread of the virus that caused symptoms of a true seizure was first recorded in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. Scientists discovered that this novel virus belonged to the family Coronaviridae and was later named as severe respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV -2). Across the globe, researchers are developing a variety of vaccines, medications, antidepressants, and many other ways to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Among various antiviral drugs, remdesivir was approved for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection. Remdesivir is a nucleoside analog that inhibits RNA-polymerase (RdRp) SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent. It is a viral polymerase inhibitor that induces the termination of both the viral transcription and fused viral genomes. However, there are some limitations that have contributed to the need to develop other antiviral drugs that will have only the greatest side effects and efficacy.
Researchers have discovered another target site of SARS-CoV-2: the 3CLpro (M.pro), a major protease. This protease plays a key role in the life cycle of the virus. After the virus enters the host cell, the RNA-positive genome of the virus is rapidly translated into two polyproteins. These polyproteins are processed into functional proteins by PL2 pro and 3CLpro viral protease. Two of the main responsibilities of 3CLpro regulates proper assembly and folding of polymerase substrate required to develop into a properly functioning polymerase substrate. With that, 3CL banpro viral life cycle was effectively stopped. Further, the specific substrate option of 3CLpro also makes it an effective target site.
So far, PF -07304814 is the only 3CLpro an inhibitor that has reached the clinical trials. It is a ketone-based covalent cysteine protease inhibitor administered as a phosphate prodrug, thus converting to its active form, PF-90 00835231. In 2003, PF-00835231 was developed in response to epilepsy coronavirus formerly as an inhibitor for the 3CLpro. However, due to the rapid decline in the disease rate, it was not taken to clinical trials, and further study of its efficacy was suspended.
Scientists believe that PF-00835231 would be effective against the novel SARS-CoV-2. This is due to a 96% similarity at the amino acid level and 100% similarity within the catalytic pocket of the 3CLpro present in both SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. A recent study showed the efficacy of PF-00835231 at high micromolar levels.
In a forthcoming paper in the Iris Virology, scientists compared the in vitro efficacy and cytotoxicity profiles of PF-00835231 and remdesivir in two human model systems for SARS-CoV-2 disease; that is, A549+ ACE2 polar human airway epithelial cells and cultures. After the first marking of A549+ ACE2 cell to study SARS-CoV-2, the in vitro was studied to evaluate the efficacy and cytotoxicity of PF-00835231, GC-376 (preclinical-grade protease inhibitor), and remdesivir in A549+ ACE2 cells.
The team also carried out time-on-drug assessments in A549+ ACE2 cells to define and compare the duration of action of antiviral drugs within the life cycle of SARS-CoV-2. The role of the Multi-Drug Resistance Protein Efflux Conveyor Protein 1 (MDR1) on the antiviral efficacy of PF-00835231 was also investigated. The main focus of the study was to deliver in vitro evidence about PF-00835231 potentially being an effective antiviral drug for SARS-CoV-2 and also clarifying its side effects based on prior studies.
This research has shown that both PF-00835231 and remdesivir are equally potent in studying a model of polarized human airway epithelial cultures (HAEC). However, in A549+ ACE2 cell assay, PF-00835231 showed superior activity than the preclinical GC-376 and similar or slightly similar effects as remdesivir.
The best time to start antiviral drug treatment is the first week after symptoms appear, ie when the reproduction of the virus is actively going on. In patients with COVID-19 side effects, active reproduction of SARS-CoV-2 may be prolonged. This study showed that intravenous treatment of PF-00835231 would still be effective for patients with severe disease. Intravenous remdesivir treatment has also been found to be effective against SARS-CoV-2.
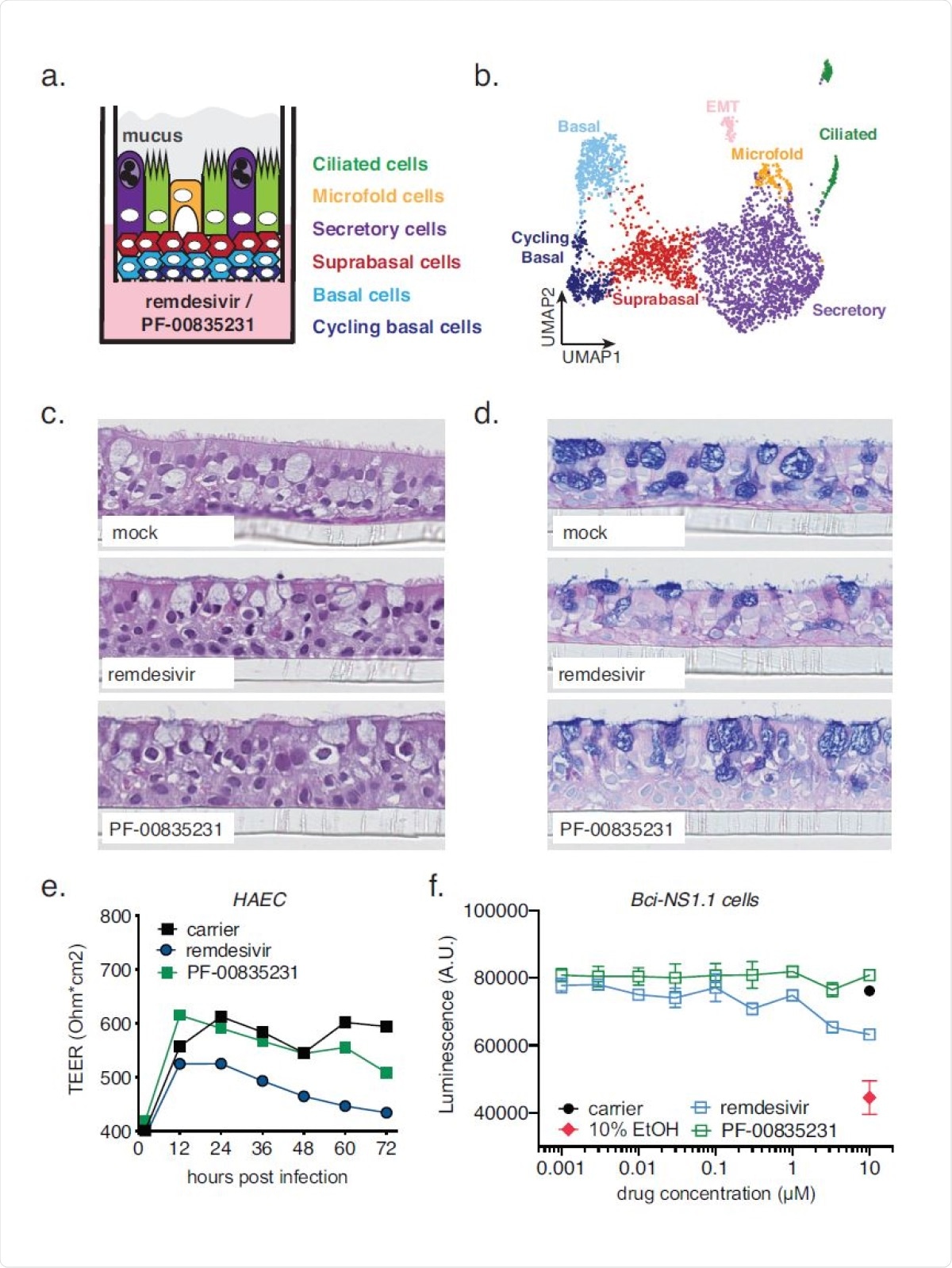
Cell production of polarized human airway (HAEC) epithelial cultures, and cytotoxicity of PF-00835231 and remdesivir. a. Decorative representation of a transwell containing polarized HAEC in an air-liquid interface. Dark blue, cycling basal cells; light blue, basal cells; red cells, suprabasal; purple, secretory cells; yellow cells, microfold; green cells, ciliated; gray, mucus. To test for cytotoxicity, drugs were added to the mediastinum in the basolateral chamber. b. Accumulated single-cell UMAP determined by single-cell RNA sequence from n = 3 unprotected HAEC. Browsers were tested with signals from the literature (37, 38) and with different signal genes for each browser validated by the Wilcox test. c., d. Representative cross-sections of unprotected HAEC, 72 h post-treatment with 10 µM PF-00835231 or 10 µM remdesivir. H&E (c.) No staining blue PAS-Alcian (d.). e. Trans-epithelial resistance (TEER) in drug1205 treated, HAEC unprotected over time as a measure of epithelial integrity. Meaning? SEM from n = 3 independent trials. f. CellTiter-glo assay on unknown, basal Bci-NS1.1 precursor cells. Meaning? SEM from n = 3 independent trials.
The current study has also revealed a significant synergistic effect between PF-00835231 and remdesivir in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2. Researchers believe that the use of multiple antiviral drugs with different modes of action or target sites would effectively circumvent mutations caused by mutations. Thus, the development of antiviral therapies using antiviral drugs would significantly improve antiviral therapy in COVID -19.
To summarize, the team’s research reveals the significance of the novel antiviral drug, PF – 00835231, against SARS-CoV-2 with the help of 3D in vitro models of human airway epithelium. This would help reduce the mortality rate of COVID-19 and also pave the way to explore new treatments for other harmful viruses.
Magazine Reference:
- Maren de Vries, Adil S. Mohamed, Rachel A. Prescott, Ana M. Valero Jimenez, Ludovic Desvignes, Rebecca O’Connor, Claire Steppan, Joseph C. Devlin, Ellie Ivanova, Alberto Herrera, Austin Schinlever, Paige Loose, Kelly Ruggles , Sergei B. Koralov, Annaliesa S. Anderson, Joseph Binder, Meike Dittmann. Comparative analysis of SARS-CoV-2 antivirals identifies 3CLpro inhibitor PF-00835231 as a potential new treatment for COVID-19, Journal of Virology Feb 2021, JVI.01819-20; DOI: 10.1128 / JVI.01819-20 https://jvi.asm.org/content/early/2021/02/19/JVI.01819-20