The coronavirus infection (COVID-19), caused by the acute respiratory coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) syndrome, is spreading worldwide. To date, more than 95 million cases of SARS-CoV-2 infection have been reported worldwide. Over the past few months, new variants of SARS-CoV-2 have emerged that are more active.
One new strain of SARS-CoV-2, called 202012/01, began spreading in England in late October. New review published on pre-print server medRxiv * found that 60 percent of daily COVID-19 cases were screened by Alderley Park Lighthouse Labs related to 202012/01, also known as line B.1.1.7 or 20B / 501Y.V1. This suggests a rapid spread of the new variety across the country.
The new variant
On 14 December 2020, health authorities in the United Kingdom and Northern Ireland reported Variant of Concern 202012/01 to the World Health Organization (WHO) after identification through a viral genomic sequence. The new variant was later noted in other countries
Although 202012/01 is considered a quick release and easy to move, it does not cause more severe symptoms.
Scientists fear that newly developed SARS-CoV-2 vaccines, some of which are already in use, may not protect against 202012/01.
In variant 202012/01 there are 14 mutations leading to amino acid changes and three mutations. One of the mutations, called N501Y, modifies amino acid within the six major residues in the receptor binding domain (RBD), making it bind more tightly to the cell receptors. This means it can catch people more easily.
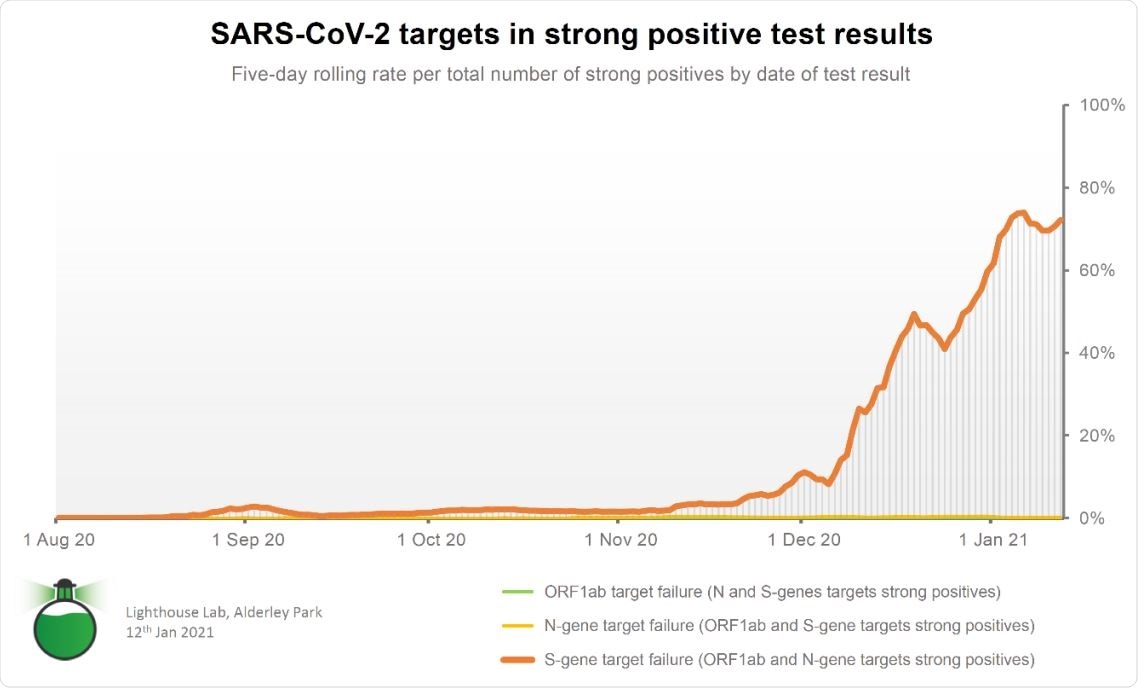
TaqPath ™ COVID 19 Assay, found S-gene compared to ORF1ab and N-gen.
In the United Kingdom alone, more than 1,100 cases of the new variant were detected by 13 December 2020. To date, 202012/01 has been reported in at least 31 countries, including Australia, Denmark, Canada, Philippines, France, Italy, Holland, Hong Kong, Japan, Singapore, and Nigeria, among others.
The study
The study, led by scientists at the Medicines Discovery Catapult, Lighthouse Labs, Alderley Park in the United Kingdom, reported that by the end of December 2020, 60 percent of daily positive test results in the laboratory were related to the a new version under review.
The Alderley Park (AP) Lab (LHL) lighthouse test for the RNA presence of SARS-CoV-2 using the ThermoFisher TagPath COVID-19 test for true polymerase transcription chain (RT-qPCR) detection SARS-CoV-2 reabsorption in nasal and throat swabs.
As the team compiled and analyzed the tests they were processing over the past few months, the impact of the new change on diagnostic tests increased rapidly in December 2020, rising to more than 70 percent. percent of strong positive test results detected in early January 2021.
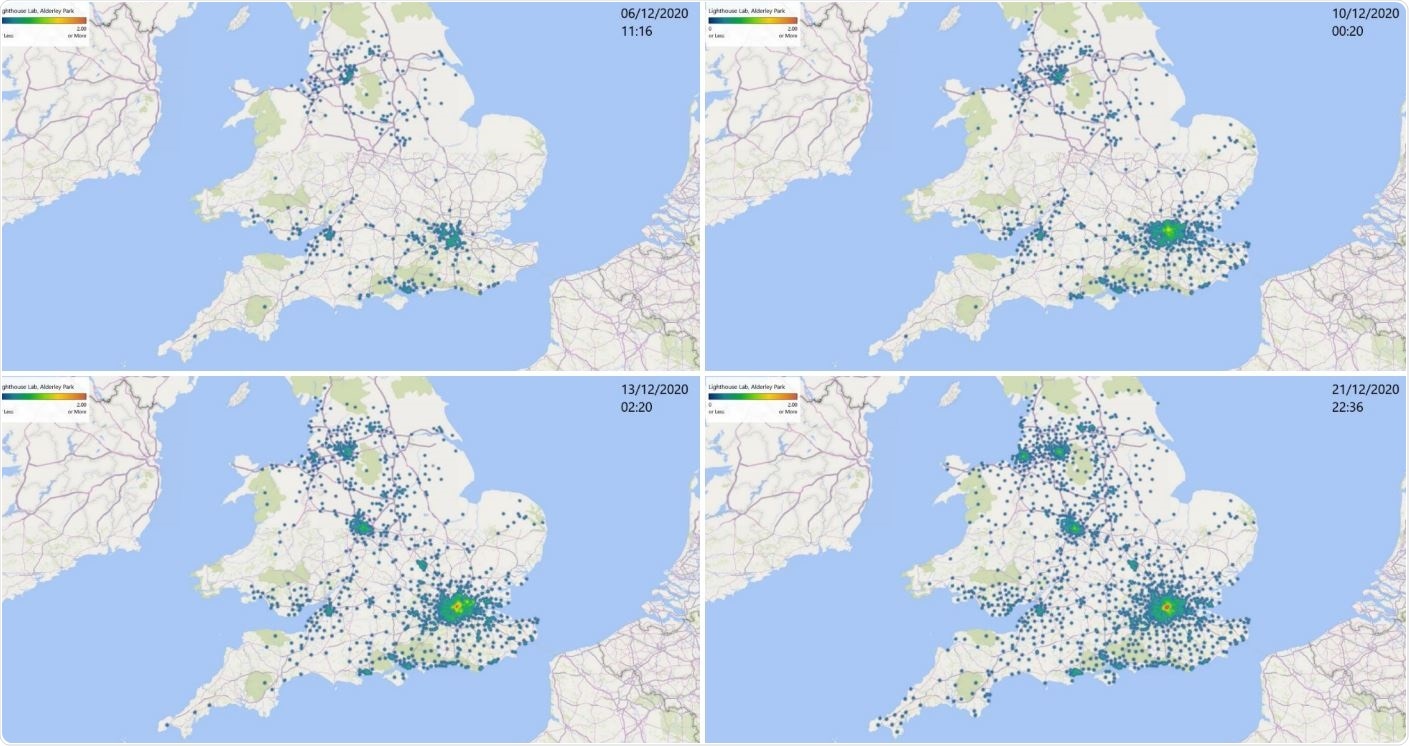
Map of S-gene detection failure, associated with the new version of SARS-CoV-2. Data collected at Alderley Park, Lighthouse Labs, from 1 to 21 December 2020.
The laboratory also noted that Spike protein mutations, typically seen in the VOC 202012/01, were present in the S-gene target detection failure cases. S-gene target detection failure is linked to the emergence of the new variant of concern. Later, some regions where the new variant was discovered are highlighted by the lack of S gene detection in the TagPath assay used in the study. This matches areas that are now reporting skyrocketing rates of patient hospitalization.
“Continuous molecular analysis will be required to ensure that other S gene mutations do not coincide with VOC 202012/01,” the researchers note in the paper.
Variable fast-scattering
The routine emergence and distribution of the new SARS-CoV-2 variant highlights the need for strengthened infection control measures. Some countries have implemented locks to prevent viral spread. Countries with COVID-19 surging issues related to the new change should also promote adherence to health protocols, including regular hand washing, social distance, and avoiding crowded places.
To date, more than 2 million deaths are linked to the pandemic worldwide. The United States reports the highest number of cases, reaching more than 24 million.
* Important message
medRxiv publish preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be seen as final, guiding health-related clinical / behavioral practice, or be treated as information established.
Source:
Magazine Reference: