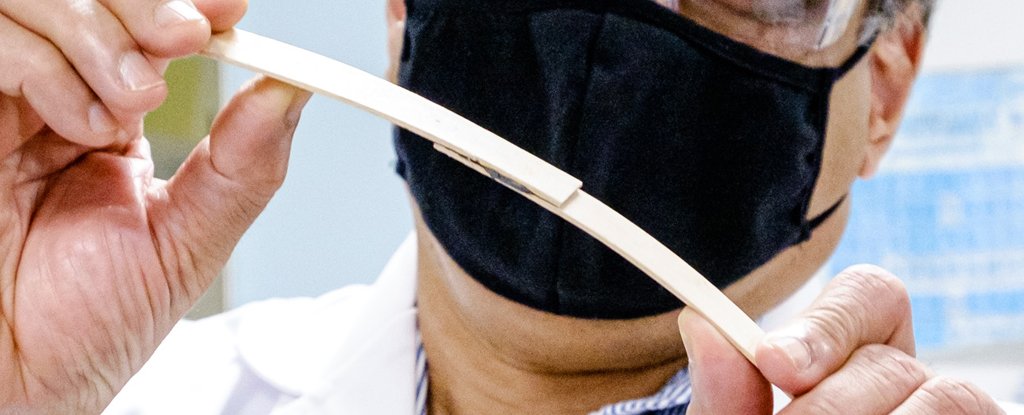
A newly developed glue that is smooth from a magnetic field could lead to significant energy and cost savings for companies that need to connect things at an industry level.
To harden – or cure – the mixture of chemicals in most epoxy – based coatings, a type of environmental effect such as heat, light or humidity must be applied.
Here, this is achieved by a “magnetocuring” process, which is encouraged as an option when conventional adhesives are not particularly effective, or in heat-sensitive applications, or for when a large amount of insulation material is involved (making it difficult to apply heat, light, or humidity).
The glue works by combining commercial epoxy with fabricated magnetic nanoparticles that mix manganese, zinc, and iron: these nanoparticles heat up when electromagnetic energy passes through, binding the materials in place.
“Our main development is a method of curing adhesives within minutes of exposure in a magnetic field, while preventing overheating of the surfaces to which they are applied, ”says materials scientist Terry Steele from Nanyang University of Technology (NTU) in Singapore.
“This is important, because some surfaces we want to assemble are highly sensitive to heat, such as flexible electronics and biodegradable plastics.”
The new glue is easier to apply, works faster, and requires less energy and space than conventional mixtures. It does not require a hardener or accelerator, and can be printed to control the maximum temperature and temperature of the heat as it is applied.
For carbon fiber products such as bicycles and helmets, for example, large ovens of the materials must be heated over many hours to cure the epoxy glue. This innovative new solution, on the contrary, requires a small electromagnetic device.
In particular, the researchers say a gram of standard epoxy glue needs to set an hour in a 2000-Watt oven. A gram of magnetocuring adhesive, by contrast, only takes 5 minutes in a 200-Watt electromagnetic device, which works out to be about 120 times less energy in total to complete the process. .
“Curing our newly developed magnetocuring adhesive only takes a few minutes instead of hours, but nonetheless it is able to get a surface with high-strength bands, which are of great interest to the sports, medical, self-adhesive industries. mobile and aerospace, ”says materials scientist Richa Chaudhary.
“This efficient process can also deliver cost savings as the space and energy required for conventional heat treatment is greatly reduced.”
The newly designed process eliminates the risk of overheating and uneven heating, and can still reach a high adhesive level of up to 7 megapascals – equivalent to the hats that are it starts to reapply. It took three years before we reached this point, and the researchers are now looking for commercial partners to work with.
Wood, ceramics, and plastics have all been tested with this magnetocuring process, making it versatile as well as highly efficient, and there are also ways that can speed up the production lines of the day. develop today.
Everything from sports equipment to aerospace components could be combined more efficiently with the new glue, the team says, and the benefits in terms of energy use and carbon emissions could be great. important, if the material can be scaled outside the laboratory.
“Our temperature-controlled magnetic nanoparticles are designed to be blended with single-pot adhesive shapes, so many of the epoxy-based hats on the market could be turned into are field-activated magnetic glues, “says materials scientist Raju Ramanujan.
The research was published in Applied Materials Today.