Even though we are know the deep sea is weird, ‘flesh-eating sea sponges’ still feel like something out of a sci-fi movie. And yet, researchers have announced that three such new species have been discovered off the coast of Australia.
Take a few hundred meters deep into the ocean, and it begins to look like you are in a whole new world: From a star-like creature crossed by an octopus, to a fish that will eating sharks, to meat-eating sponges we’ve never seen it.
“It just shows how many of our deep oceans remain to be explored – these special sponges are very special as they are only found in this special area of The Great Australian Bight – an area that has been slated for oil exploration. deep sea, ”said one of the researchers, manager of the Queensland Museum Sessile Marine Invertebrate Collection Merrick Ekins.
Sea sponges usually feed on heterogeneous sieves – they have holey turf for flowing water, from which their cells secrete oxygen and food. They are very simple creatures, with no nervous, digestive or circulatory system, but they have been in some form for over 500 million years.

But carnivorous sponges are a little different. Some carnivorous sponges still use the water flow system, but others (such as the three recently discovered species) have completely lost this ability, including small crustaceans and prey. others using filaments or hooks.
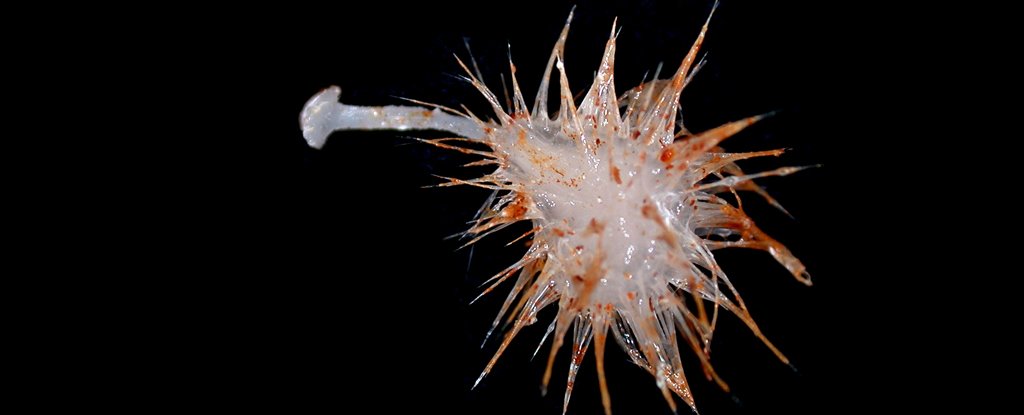
The researchers in this study discovered three new species of carnivorous sponges – Nullarbora heptaxia, Abyssocladia oxyasters and Lycopodina hystrix, which are also all new genes, as well as a closely related non-carnivorous sponge species, Guitarra davidconryi. All of these species have been found at depths between 163 and over 3,000 meters (535 to 9,842 feet) deep.
“Here we report on four new species of sponges found from the Great Bight of Australia, South Australia. This area has recently been surveyed, using a Smith-McIntyre Grab and a Vehicle that has sudden operation (ROV) to pick up and harvest the marine biota., “the researchers write in their new paper.
“These new species are the first recorded carnivorous species from South Australia and will increase the number of species recorded from around Australia to 25.”
The sponges are also better than you might think, look somewhat like flowers with their spiky protrusions, but they are not at all like sponges.

Carnivorous sponges get a few minutes. We have known about them since 1995, but many more have been discovered around the world.
“Over the last two decades, our knowledge of the diversity of meat-eating sponges has almost doubled,” the same team explains in an earlier paper, where they described the they discovered 17 new species of carnivorous sponges.
“[This is] partly as a result of rapid advances in deep-sea technology including ROVs and submersibles capable of picking up and harvesting carnivorous sponges, and also to the herculean efforts of a number of contemporary taxi drivers. many of the ancient species described in the 19th and 20th centuries. “
Almost every species of carnivorous sponge found in Australia was discovered during a CSIRO RV research trip in 2017, demonstrating the importance of these deep-sea studies.
With the ocean floor still largely unexplored, we think we’ll see many more species of carnivorous sponges, and other weird and wonderful sea creatures.
The research was published in Zootaxa.