
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I will review changes to the Advisory Committee on Vaccine Practices (ACIP) Adult Vaccination Schedule for 2021, which was published in the History of internal treatments.
Each year, ACIP updates its summary of recommended vaccinations for adults. This year, ACIP held more than three times the normal number of meetings (10 meetings instead of the usual three). Seven of these meetings were dedicated exclusively to the COVID-19 vaccine review and plans for vaccine administration.
So, the first thing more than the 2021 record is no surprise. COVID vaccines are included in the vaccine notes section with a link to ACIP interim recommendations for the use of COVID-19 vaccines.
Section 3203 of the CARES Act requires coverage of COVID-19 vaccines recommended by ACIP. A special language in the register is required to ensure that any administrative costs are covered by insurance.
For the first time, ACIP workshops for the adult and for child / adolescent timetables have been combined in an effort to harmonize the appearance of the graphics and the language in the notes, where possible.
The color-coded key used to name vaccines that are “delayed until after pregnancy” is marked with a red star. Other color codes are the same:
-
Yellow: Recommended
-
Purple: Award if an additional risk feature is present
-
Orange: Precautions
-
Blue: A recommendation based on shared clinical findings
-
Red: Not recommended / contraindicated; the vaccine should not be given. Star also adds language: Vaccinate after pregnancy
-
Gray: Not recommended / not applicable
New for 2021
Blessing with live zoster vaccine (ZVL; Zostavax). It has been removed from the register. As of July 2020, it is no longer available in the United States. The remaining stocks left in November 2020.
A new adult vaccine, MenQuadfi, offers another MenACWY vaccine product option.
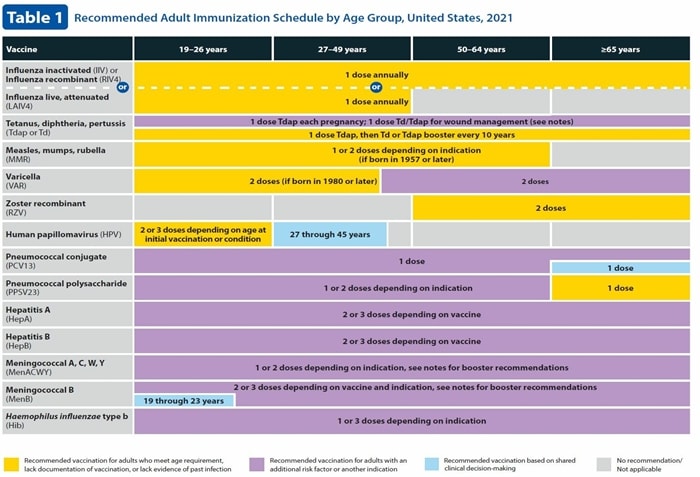
Table 1. Vaccines by age. Download a PDF here
Td or Tdap is now divided into purple and yellow color codes. The yellow bar indicates that a normal increase is required every 10 years. Purple supplementation marks Tdap in all pregnancies and Td or Tdap for injured prophylaxis. Details of tetanus for injury management are included in the notes, along with a link to the overall recommendation.
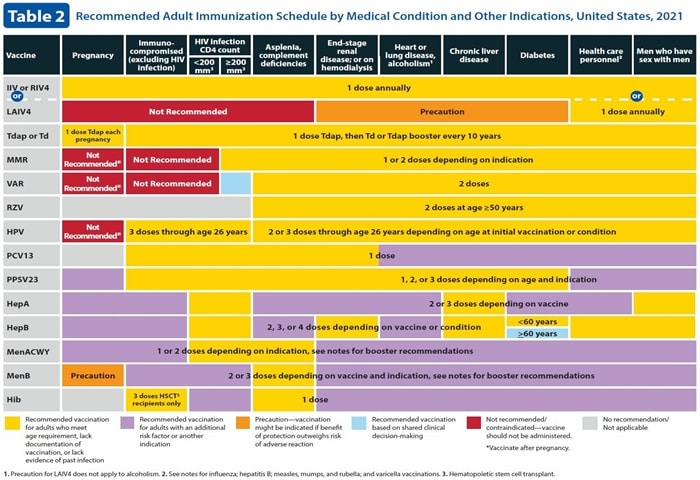
Table 2. Vaccines according to medical condition and other symptoms. Download a PDF here
Here, there are two broad variations. Pink is outside, and blue is inside to indicate shared results, replacing yellow for varicella vaccination for those living with HIV with CD4 counts of 200 cells / mm3 and higher. Shared clinical findings are needed for the use of this live virus vaccine in vaccinated patients.
Hepatitis B vaccine for patients with diabetes aged 60 and older is now coded blue, reflecting shared clinical findings. For patients with diabetes under 60, the hepatitis B vaccine is still yellow – coded, indicating that all patients aged 60 and under should have diabetes.
There are major changes in the pregnancy column of Table 2. The use of pink 2020 to delay vaccination until pregnancy is replaced, means that the vaccine is not recommended during pregnancy. This applies to the HPV vaccine as well as other live virus vaccines: MMR, varicella, and LAIV. The recurrent zoster vaccine (RZV; Shingrix) is now gray-coded, meaning it is not recommended.
Vaccine notes
The “Vaccine notes” section contains editorial changes aimed at matching language between the timetables of children / teenagers and the one for adults.
Under the flu vaccine note, the section on those with egg allergies has been revised. Language before said that people with a history of hard egg allergy would need to be in a medical condition when you receive the vaccine. New language says that this medical condition caveat is not necessary for those with severe egg allergy to get the eggless Flublok or eggless Flucelvax.
The combination of flu antivirals with different half-lives led to additional language about the interval between LAIV and influenza antivirals: LAIV should not be used if the patient has receiving an antiviral medication (oseltamivir or zanamivir) in the previous 48 hours, peramivir in the previous 5 days, or baloxavir in the previous 17 days.
For travelers, an accelerated dosing schedule was introduced for hepatitis A / B (Twinrix) prior to travel, with preference for doses at 0, 7, and 21-30 days and an increase in 12 months.
Interim proposals
CDC interim clinical recommendations recommend aiming for a 2-week window between COVID vaccine and other vaccine doses, if possible. This will help give COVID mRNA vaccines the best chance of stimulating an immune response. However, tetanus augmentation can be accepted for wound management or a dose of MMR or hepatitis A vaccine during measles or hepatitis A. We do not want to delay the implementation of COVID mRNA vaccines.
Vaccines do not save lives; make vaccines!
For Medical Issues, I am Dr. Sandra Fryhofer.
Follow Medscape on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and YouTube